Elon Musk famously said, “Empathy is not an asset”.
Musk learned this from the video game Polytopia, which he played with his brother, coworkers, and partners. He made a list of life lessons from the game, which he calls Polytopia Life Lessons.
Musk’s indifference to empathy is not isolated when you look at notoriously ruthless business leaders such as Jeff Bezos, Bill Gates, and Steve Jobs. They have all had difficulties with interpersonal dynamics and yet been incredibly successful by the mainstream’s definition of success.

Are You Truly Leading or Just Managing? You Need Real-Time Feedback
Are You Truly Leading, or Just Managing? The Case for Real-Time Feedback


Grant Ian Gamble is a best-selling mindful leadership author and speaker. He has over 30 years of experience in leading teams to create innovative customer experiences, building engaged workforces, and developing leaders who prioritize people, workplace wellbeing, and mindfulness in their approach.
Great leadership is a journey. Yet, many top-tier leaders fall into the trap of believing they have arrived. After years of experience and success, it is easy to assume that your leadership is foolproof.
But true leadership is not about titles or tenure—it is about service, adaptability, and a relentless commitment to growth.
The best leaders do not operate in an echo chamber. They do not rely on assumptions or past successes to guide their decisions. Instead, they actively seek feedback—real-time, honest, unfiltered feedback—from both their Team Members and Customers. They understand that leadership is not about them—it is about the people they serve.
Servant Leadership: The Commitment to Growth
 A servant leader does not just want to lead; they want to lead well. They do not fear constructive criticism; they welcome it. They understand that blind spots and biases exist, and the only way to uncover them is through consistent, real-time insights from those they impact most: their Team and their Customers.
A servant leader does not just want to lead; they want to lead well. They do not fear constructive criticism; they welcome it. They understand that blind spots and biases exist, and the only way to uncover them is through consistent, real-time insights from those they impact most: their Team and their Customers.
In my book, The Affinity Principle, I introduce the AFFINITY Formula:
Mindful Leadership → Team Member Engagement & Well-being → Customer/Member Experience → Retention & Referrals → Sustainable Growth
This formula is a simple yet profound truth. Great Leaders create thriving Teams. Thriving Teams create outstanding Customer experiences. Outstanding Customer experiences build Community, drive Retention and Referrals, which fuel long-term business Success. But at the heart of this equation is a leader’s ability to stay connected to their people—by listening, adapting, and leading with intention.
Why Real-Time Feedback Matters
For Leadership to be truly effective, it must be rooted in data, context, and sentiment—not just gut feelings or periodic reviews. That is where real-time feedback systems come in. They allow leaders to:
- Gauge Team Member Engagement & Well-being before burnout, disengagement, or turnover occurs.
- Monitor Customer/Member Experience in real time, addressing concerns before they become retention and attrition risks.
- Improve decision-making based on live data, rather than waiting for outdated or incomplete reports.
- Create a culture of continuous improvement where feedback is not an event but an ongoing dialogue.
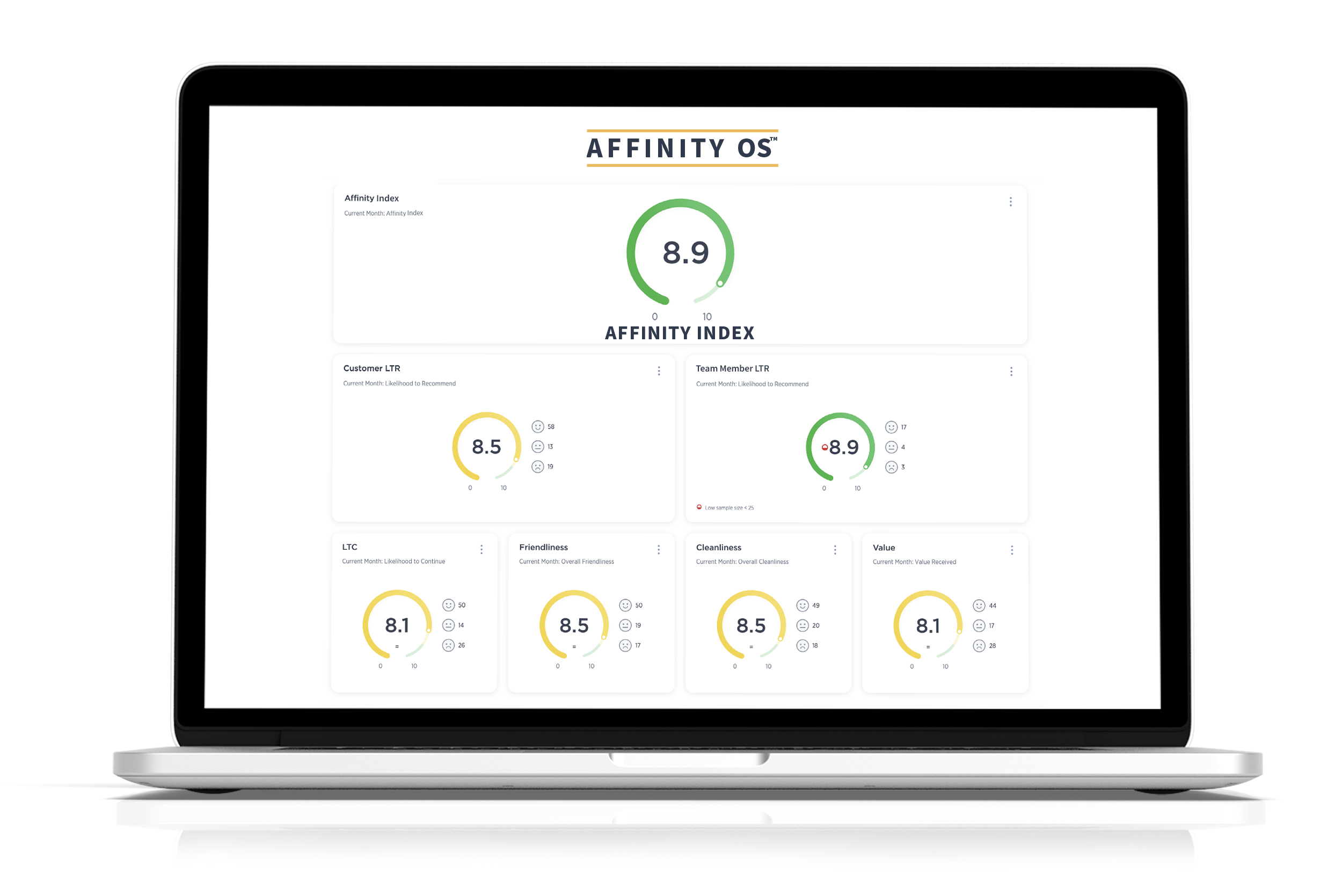
The AFFINITY OS™ Advantage
This is exactly why we built AFFINITY OS—an AI and human-driven business intelligence system designed for Mindful Leaders who want real-time, Actionable Insights. It does not just provide metrics; it provides sentiment analysis—the context behind the data. It completes the crucial feedback loops between leaders, Team Members, and Customers/Members, ensuring businesses remain agile, responsive, and people-first.
When leaders have access to real-time engagement and experience data, they are not guessing—they are leading with Clarity, Precision, and Impact.
People-First Leadership Drives Growth
The most successful businesses in the world are built on people-first leadership. It is not about managing processes; it is about inspiring people. When leaders prioritize engagement, well-being, and experience, they do more than drive results—they create legacies.
So ask yourself: Do you truly know how you are doing as a leader? If the answer is not based on real-time feedback from your Team and Customers, it may be time to rethink your approach. Because great leadership is not about having all the answers—it is about having the courage to ask the right questions.
#1 Secret to Your Wellness Business Success in 2025


 Interested in learning more about how to transform your organization’s approach to team member engagement and customer experience? Reach out to our team at AFFINITY OS, specialists in AI-driven customer experience and team member engagement optimization.
Interested in learning more about how to transform your organization’s approach to team member engagement and customer experience? Reach out to our team at AFFINITY OS, specialists in AI-driven customer experience and team member engagement optimization.
Put PEOPLE FIRST, ALWAYS and watch your business flourish.
Dive deep into the latest trends in customer experience and team engagement, mindful leadership and management. Discover practical tools and strategies that you can use to build a people-centric culture, the foundation for sustainable long-term business growth and success.
Led by mindful leadership expert, Grant Ian Gamble, a best-selling author and true visionary with over 30 years of experience in leading teams to create innovative customer experiences, building engaged, inspired and fulfilled workforces, and developing leaders who prioritize genuine connection in their approach.
The guiding principle behind all of Grant’s work is PEOPLE FIRST, ALWAYS.
More Articles:
Is Elon Musk Wrong?
Embrace Workplace Wellbeing: Navigate Stress, Anxiety, Overwhelm and Burnout with AFFINITY OS’s™ NEW Psychosocial Risk (PSR) Management Tool
A state of stress, anxiety, overwhelm and burnout feels almost endemic these days. I hear it from friends, family members, work mates and peers. The pressures seem to come from all directions—work, media, global events, and personal life demands. Everywhere you turn, there’s more information, more conflict, more polarization, more uncertainty and it feels as if it’s escalating, relentlessly. This growing sense of overwhelm isn’t just affecting individuals; it’s affecting entire organizations, from the mental wellbeing of team members and tenure to overall workplace productivity.
Why Sales May Seem Easier Than Retention in the Fitness Industry
In the fitness industry, sales often grab the spotlight due to their immediate results and clear metrics, like quick sign-ups and instant revenue boosts. However, as industry leaders, it’s crucial to understand why retention might seem less controllable but is equally vital for sustainable success.
Fill out the form below and receive a PDF download of "6 Key Strategies to Engage Untapped Fitness and Wellness Market Segments"
Let's Connect!
CUSTOMER EXPERIENCE, TEAM ENGAGEMENT & WORKPLACE WELL-BEING: AFFINITY OS™ | WELLNESS INTEGRATION | MINDFUL LEADERSHIP: "THE AFFINITY PRINCIPLE"
0475 866 592

The Affinity Principle™ by Grant Gamble presents a formula for business success through a people-centric, mindful leadership approach.
PEOPLE FIRST, ALWAYS.